Interpretation:
*Please consult and check with your doctor. No Need to get panic before consulting with your doctor. I believe these are just numbers for people not from medical background. Dont assume anything your own.
ESR is also known as Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate. An ESR test is used to assess inflammation in the body. Many conditions can cause an abnormal ESR, so an ESR test is typically used with other tests to diagnose and monitor different diseases.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a blood test that measures how quickly red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle at the bottom of a test tube that contains a blood sample. It is a non-specific test that can indicate inflammation in the body due to various causes, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, cancers, and blood disorders.
Normally, red blood cells settle slowly in the test tube, but certain factors can make them clump together and fall faster. These factors include increased levels of proteins called acute phase reactants, which are produced by the liver during inflammation. The ESR test can help diagnose or monitor conditions that cause inflammation, but it cannot identify the specific cause or location of the inflammation. Therefore, it is usually used along with other tests and clinical information.
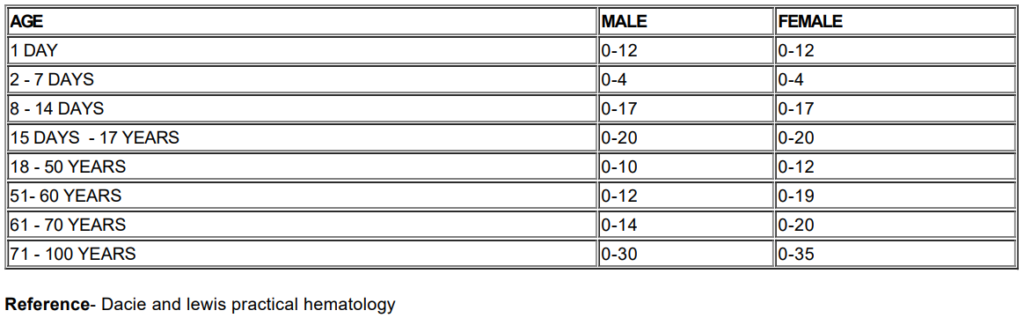
The ESR test is simple and involves taking a blood sample from a vein in your arm. The blood sample is then placed in a tall, thin tube and left undisturbed for one hour. The distance that the red blood cells have fallen from the top of the tube is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/hr). The normal range of ESR varies depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally it is less than 15 mm/hr for men and less than 20 mm/hr for women.
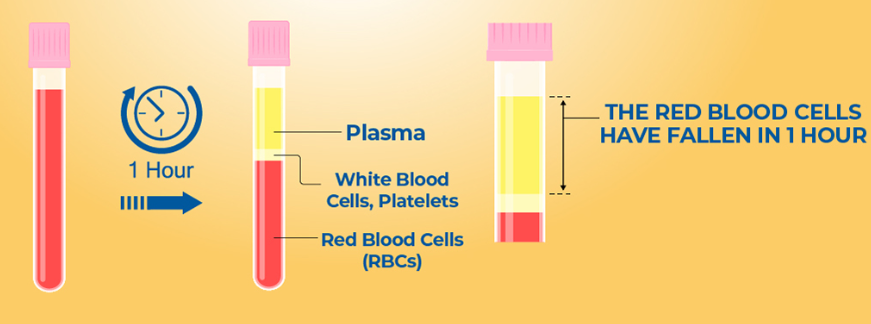
*This image copied from Dr Path lab
A high ESR indicates that there is inflammation in the body, but it does not tell what is causing it. Some of the conditions that can cause a high ESR are:
An elevated ESR may occur in inflammatory conditions including infection, rheumatoid arthritis ,systemic vasculitis, anemia, multiple myeloma , etc. Low levels are typically
seen in congestive heart failure, polycythemia ,sickle cell anemia, hypo fibrinogenemia , etc.
- Infections, such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, or endocarditis
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or temporal arteritis
- Cancers, such as lymphoma, multiple myeloma, or ovarian cancer
- Anemia, especially iron deficiency anemia or hemolytic anemia
- Kidney disease, such as nephrotic syndrome or chronic kidney failure
- Pregnancy, especially in the third trimester
- Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
A low ESR indicates that there is less inflammation in the body, but it can also be caused by some conditions that affect the shape or number of red blood cells, such as:
- Leukocytosis, which is an increase in the number of white blood cells
- Polycythemia, which is an increase in the number of red blood cells
- Sickle cell anemia, which is a genetic disorder that causes abnormal red blood cells
- Congestive heart failure, which is a condition that affects the pumping of the heart
- Hypofibrinogenemia, which is a low level of fibrinogen, a protein involved in blood clotting
- Hypoalbuminemia, which is a low level of albumin, a protein that helps maintain fluid balance in the blood.
The ESR test is not a definitive test for any condition, and it can be affected by many factors, such as medications, diet, menstrual cycle, and physical activity. Therefore, it is important to interpret the results in the context of your medical history, symptoms, and other test results. Your doctor can explain what your ESR test results mean and what further tests or treatments may be needed.
One of the standard range of ESR based on age and sex is as below,